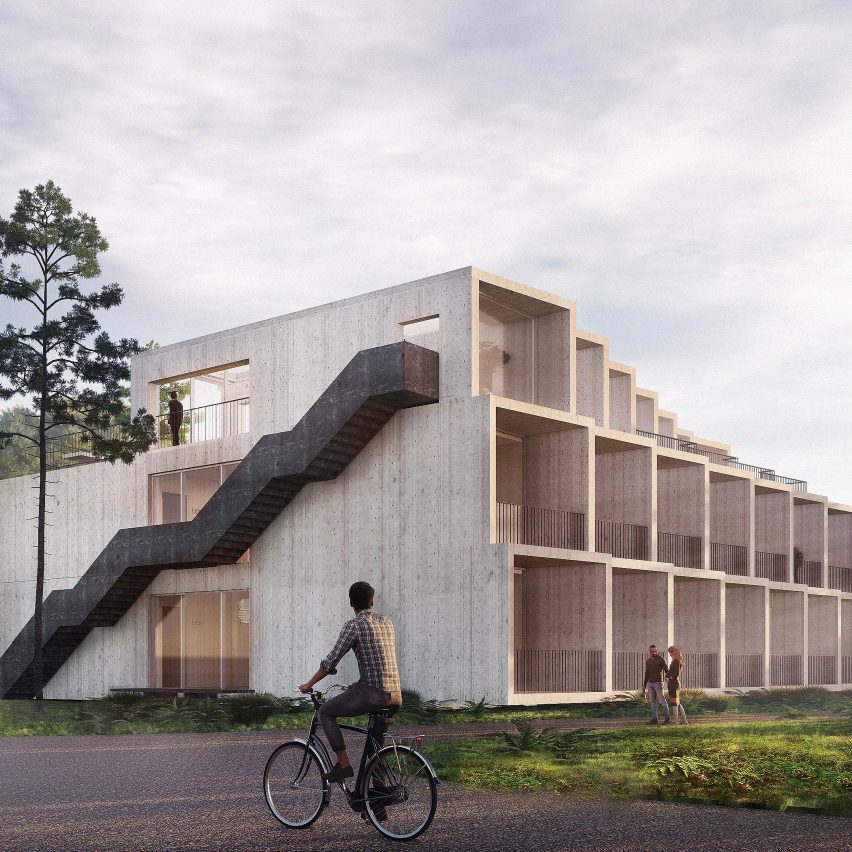
Sequestering carbon that has been far away from the ambiance in buildings and merchandise is a key means of tackling climate change.
This may be finished by taking plant matter reminiscent of wood, cork, hemp, and algae that have captured atmospheric carbon through photosynthesis and utilizing it instantly. Alternatively, it may be was different supplies that retailed carbon extra completely.
“What if every little thing we’re surrounded with was eradicating emissions as a substitute of releasing them?” stated Neema Shams of Made of Air, which makes carbon-negative bioplastic from forest and agricultural waste.
The fabric is carbon-negative as a result of it comprises extra carbon than was emitted through the materials’s manufacture and use.
Listed below are ten examples of carbon-storing supplies from our archive.
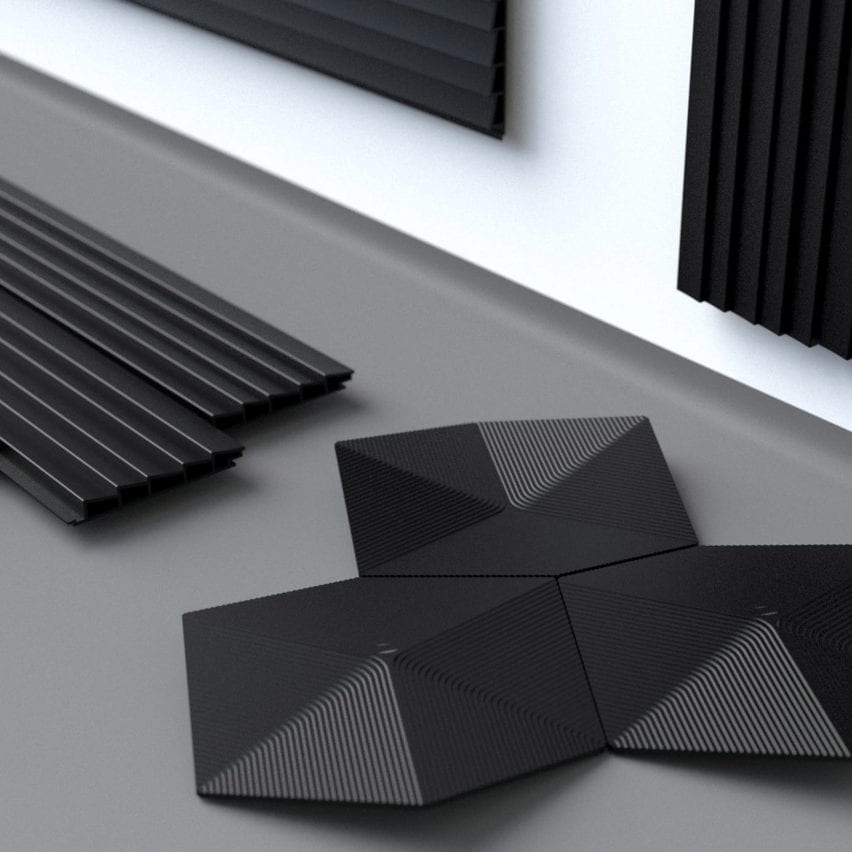
Bioplastic
German model Made of Air has developed a carbon-negative bioplastic that can be utilized in vehicles, interiors and cladding.
The fabric comprises biochar, a carbon-rich substance made by burning biomass with out oxygen, which prevents the carbon from escaping as CO2.
“With biochar, in case you simply left it on the bottom and got here again a thousand years later, it might look precisely the identical,” Shams stated. “Provided that you had been to burn it might that carbon be re-released.”
The bioplastic was not too long ago used to clad a automotive dealership in Munich with the set up storing 14 tonnes of carbon, in line with Made from Air.

Mycelium insulation
Begin-ups together with London-based Biohm are utilizing mycelium to create constructing insulation that’s naturally fire-retardant and removes “at the least 16 tonnes of carbon per 30 days” from the ambiance because it grows.
Mycelium, a biomaterial that varieties the basis system of fungi, feeds on agricultural waste and within the course of sequesters the carbon that was saved on this biomass.
Sustainability skilled David Cheshire described mycelium as “a part of the answer” to creating buildings carbon-negative.
“It is naturally fireplace retardant,” he told Dezeen. “It is truly bought higher insulation properties than most traditional insulation and it is truly sequestering carbon.”
Mycelium is fast-growing and low cost to provide in custom-made bioreactors. It may be grown in moulds to create usable merchandise reminiscent of packaging and lamps.
It will also be was new supplies together with leather-like products such as Mylo. These in flip can be utilized to provide handbags and clothes.
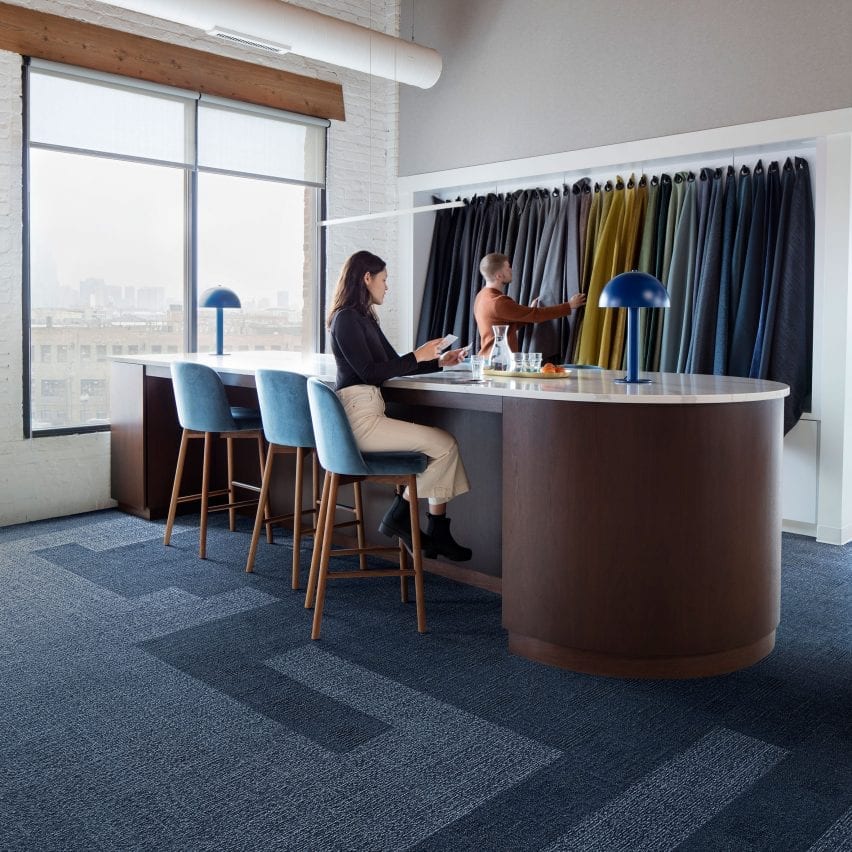

Carpet tiles
American carpet-tile producer Interface is aiming to make its whole product vary carbon adverse by 2040, beginning with the Embodied Magnificence and Flash Line carpets that had been launched this yr.
They’re constructed virtually solely from recycled plastic and numerous biomaterials, which the model says retailer extra embodied carbon than is emitted by the merchandise of their manufacturing.
Interface describes the tiles as carbon-negative “from cradle to gate”, which means their lifecycle after they depart the manufacturing unit shouldn’t be taken under consideration.
“It is not carbon-negative for its full lifecycle as a result of parts of transport and end-of-life use we will affect however we will not management at this stage,” Interface sustainability leader Jon Khoo told Dezeen.
“So we needed to deal with going carbon adverse with what we will management.”
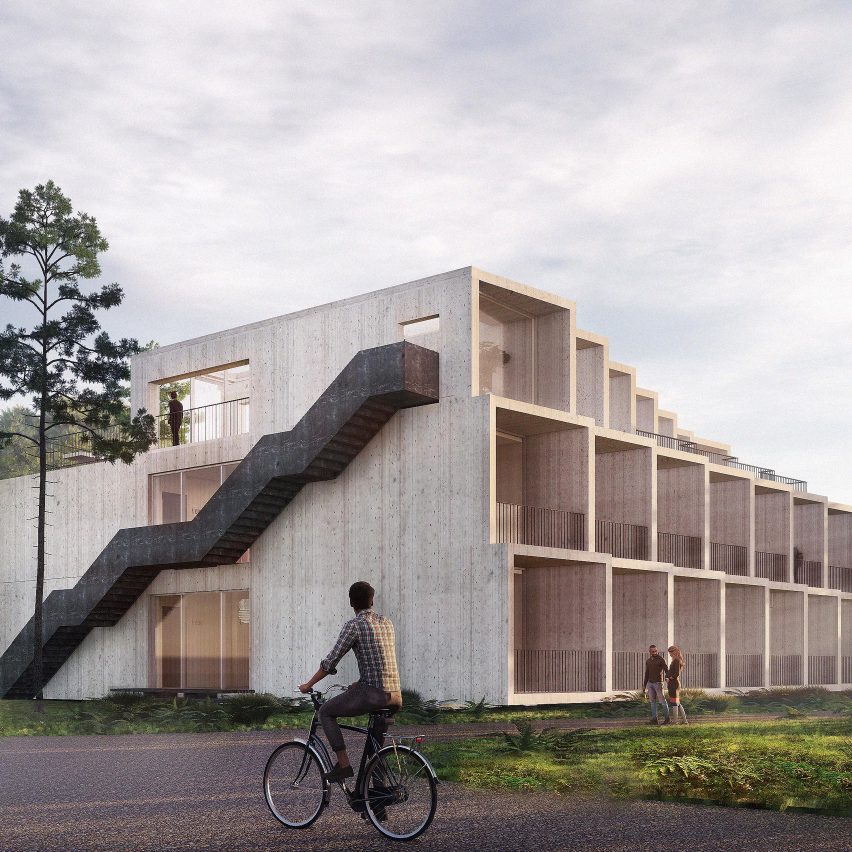

Wooden
A totally-grown tree can take away 22 kilograms of CO2 from the ambiance over the course of a yr, which means that the fabric is carbon adverse so long as it’s responsibly sourced and that the felled tree is compensated by new planting.
Any carbon saved within the wooden must be weighed towards the emissions generated throughout transport and processing and substitute bushes should be left rising lengthy sufficient so that they themselves will be harvested and was carbon-storing supplies.
Nonetheless, one drawback with wooden is the super quantity of waste produced by the timber business. Solely a part of every tree is used and processing timber generates important quantities of offcuts and sawdust. As well as, solely round 10 per cent of timber is recycled.
“Simply take into consideration carving wooden,” stated sustainable-design guru Willian McDonough in an interview with Dezeen as part of carbon revolution. “It is a adverse course of, proper? We’re slicing away stuff on a regular basis.”
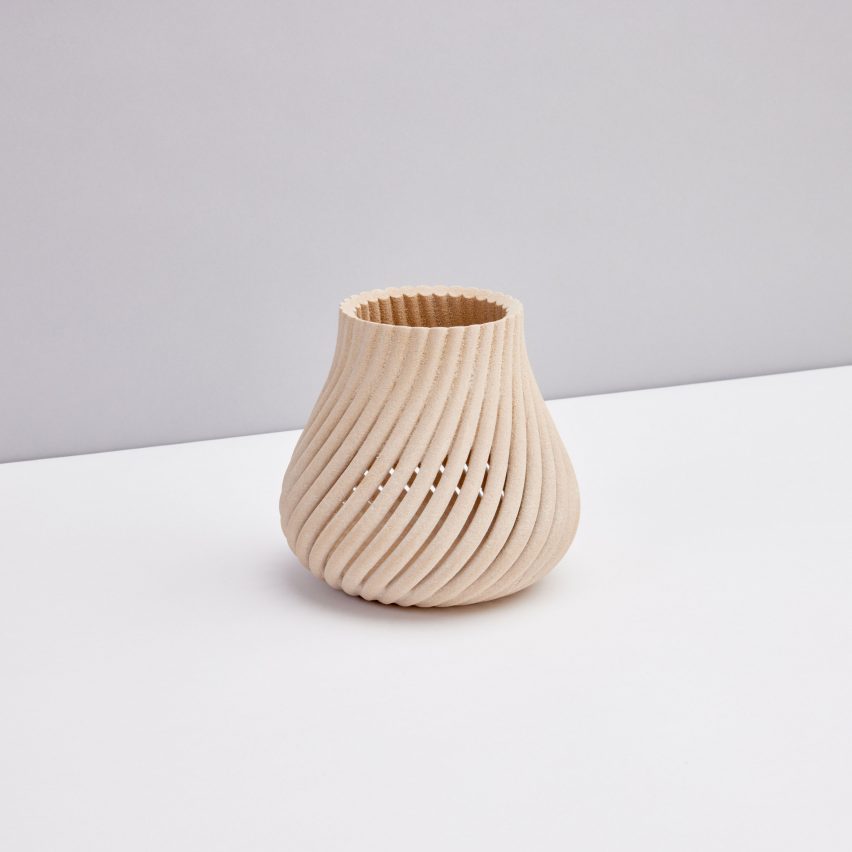

3D-printed wooden
Additive manufacturing firm Forust has developed a means of turning sawdust and lignin discarded by the timber and paper industries right into a 3D printing filament.
By making merchandise from waste, the corporate hopes to cease further bushes from being lower down in addition to stopping the waste wooden from decaying or being incinerated, which might re-release the carbon is saved.
“It may save a variety of bushes,” stated McDonough. “It is form of enjoyable and it is fairly lovely.”
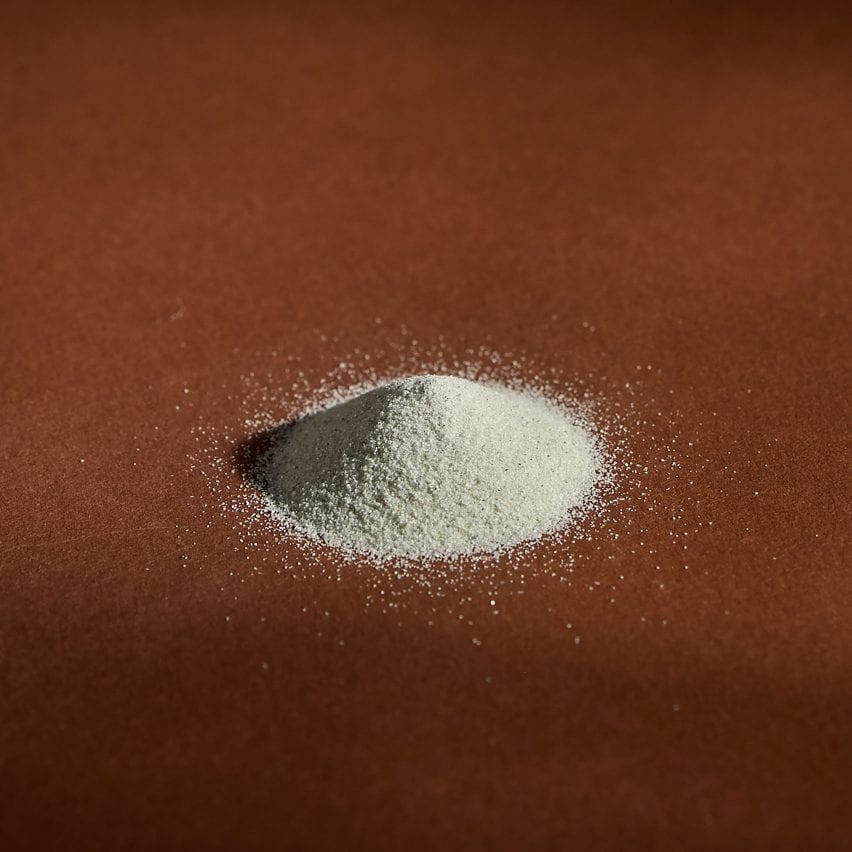

Olivine sand
Olivine, which is among the most typical minerals on earth, is able to absorbing its personal mass in CO2 when crushed and scattered on the bottom.
This implies it lends itself to being a fertiliser and a substitute for sand or gravel in landscaping, whereas the carbonated model (above) can be utilized as an additive within the manufacturing of cement, paper or 3D-printing filaments.
“It absorbs CO2 very simply,” stated Teresa van Dongen, who has included the mineral in an online library of carbon-capturing materials.
“One tonne of olivine sand can soak up as much as one tonne of CO2, relying on the situations. You simply need to unfold it out and nature will do its job.”
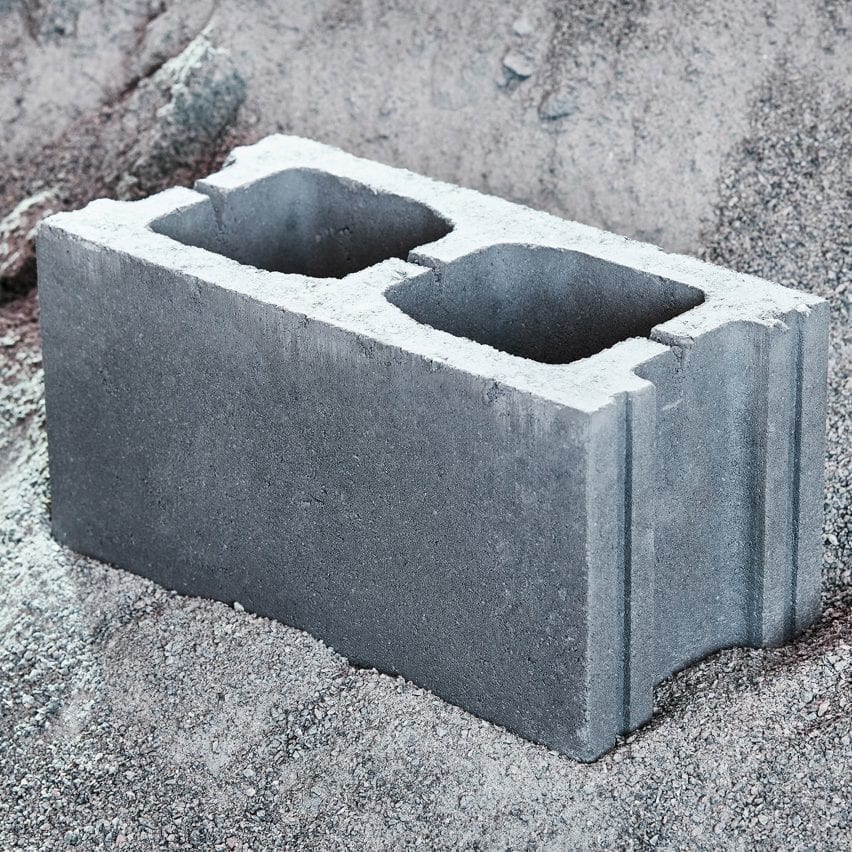

Concrete
Montreal firm Carbicrete has developed a sort of concrete that captures carbon in its manufacturing whereas substituting emissions-intensive cement, which is liable for eight per cent of all greenhouse gasoline emissions, with waste slag from the metal business.
At present, the method depends on captured industrial emissions, which means that it reduces the quantity of latest emissions being pumped into the ambiance however doesn’t scale back atmospheric CO2. Nonetheless, as soon as the corporate attracts its CO2 from the ambiance through direct air seize (DAC), this may make the ultimate materials carbon-negative.
“It is adverse emissions,” Carbicrete CEO Chris Stern told Dezeen. “We’re taking CO2 out of the system each time we make a block.”
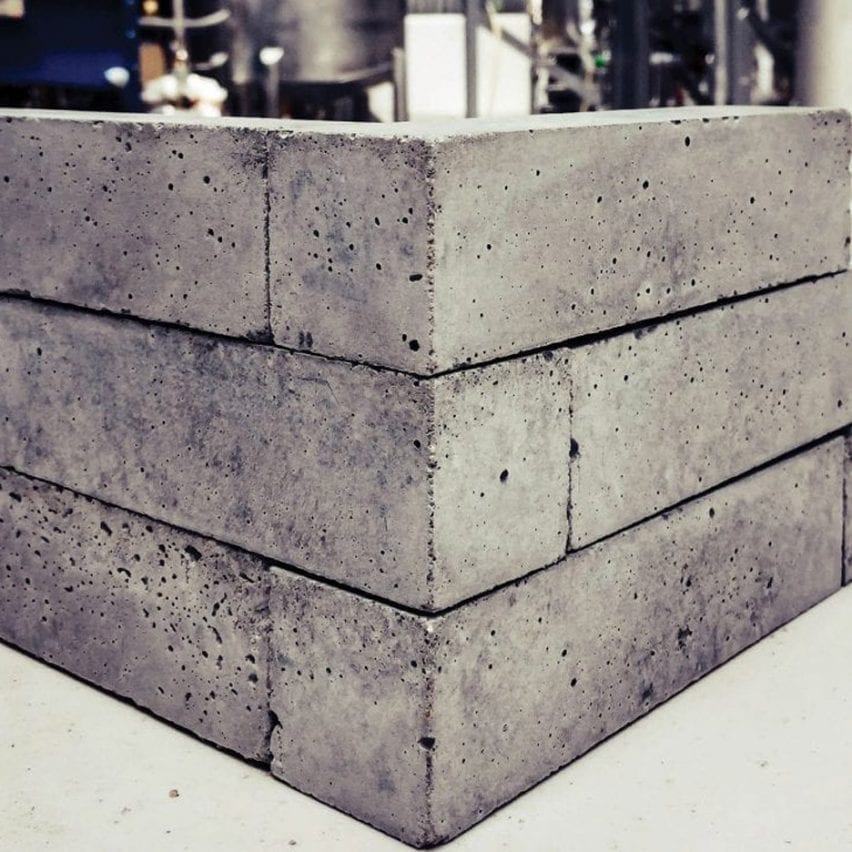

Bricks
Australian firm Mineral Carbonation International injects CO2 into industrial waste reminiscent of mine tailings, turning it from a gasoline right into a stable that may then be used to create cement bricks and different constructing supplies.
The method replicates the identical mineral carbonation course of that takes place in nature as carbon dioxide dissolves in rainwater and reacts with rocks to kind new carbonate minerals.
“We’re making an attempt to embed emissions into as a lot of our on a regular basis life as potential,” said MCi chief operating office Sophia Hamblin Wang. “We flip waste into new merchandise. And we purpose to do it in a means that makes cash.”
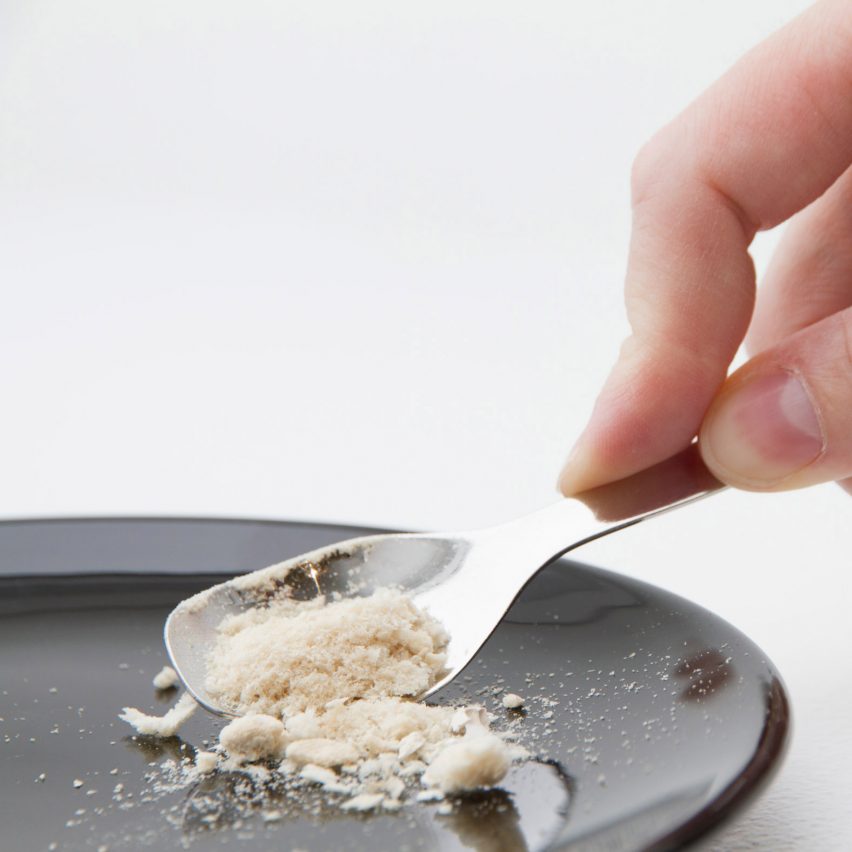

Meals
Solar Foods is one in all a rising cohort of firms utilizing emissions captured from industrial vegetation to create meals and drinks. The Finnish firm makes use of microbes to show carbon dioxide right into a meat substitute referred to as Solein.
The CO2 is injected right into a fermentation tank along with hydrogen and totally different vitamins, all of which the microbes eat and switch into protein that’s then harvested and dried, leading to a powder with the same composition to dried soy.
The carbon dioxide at the moment comes from business however may one come from captured atmospheric carbon.
If scaled up, the know-how may doubtlessly present humanity with its protein wants whereas utilizing a fraction of the land and assets utilized by conventional agriculture, thereby liberating up extra land for afforestation, solar energy and different technique of tackling local weather change.
Producing Solein is solely free from agriculture,” stated Photo voltaic Meals. “It does not require arable land or irrigation and is not restricted by local weather situations.”
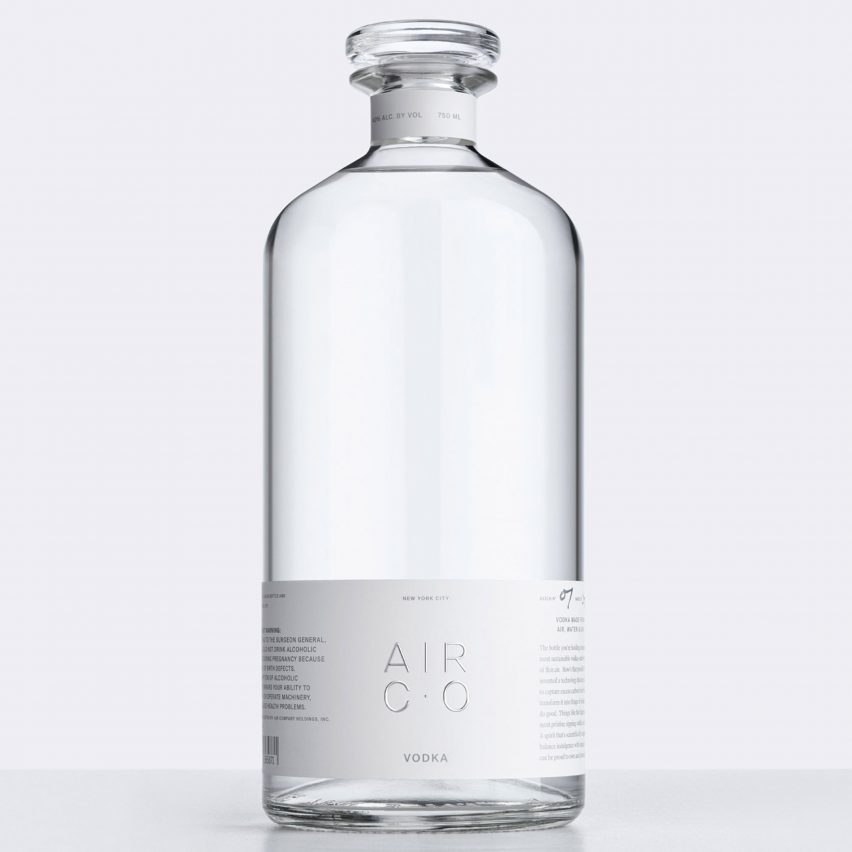

Vodka
Brooklyn-based Air Co makes use of CO2 to make vodka. The model breaks down carbon dioxide with water and a proprietary catalyst in a reactor to create ethanol, which is then used to distil vodka.
“We invented a technique to seize extra carbon from the air and switch it into ultra-refined, covetable merchandise,” Air Co stated, though the declare is deceptive for the reason that CO2 comes from manufacturing unit emissions, which means it reduces fairly than reverses greenhouse-gas emissions.
As well as, food and drinks solely provide short-term storage of carbon, for the reason that product is quickly consumed and the carbon returned to the ambiance through the pure carbon cycle.

Carbon revolution
This text is a part of Dezeen’s carbon revolution collection, which explores how this miracle materials might be faraway from the ambiance and put to make use of on earth. Learn all of the content material at: www.dezeen.com/carbon.
The sky {photograph} used within the carbon revolution graphic is by Taylor van Riper through Unsplash.




